What are the security features to look for in a payment processor?

Digital security breaches and attacks are no joke. According to the ACSC, the average cost per cybercrime in the 2021-2022 financial year rose to over $39,000 for small businesses. Meanwhile, IBM’s 2023 ‘Cost of a Data Breach Report’ put the global average cost of a data breach at US$4.45 million. This was based on a study of 553 businesses impacted by this type of attack.
The good news is that there are plenty of ways that businesses can protect themselves. This includes partnering with a reliable payment processor that implements strong security measures. Let’s explore what security features you should look for when choosing a payment acquirer, to put you in the best possible position for a future free from unpleasant surprises.
Why is payment security so important?
Payment providers handle large volumes of customers’ sensitive personal and financial information, so security is paramount. The payment technology you choose will also be in charge of settling payments into your own company account. For this reason, there are many risks associated with payments, which must be mitigated to ensure the continued success of the business.
These risks include:
Financial losses for businesses: Dealing with chargebacks and refunds after unauthorised or fraudulent uses of personal financial information is costly both in times of money and team resources.
Loss of customer trust and reputational damage: This can lead to a decline in sales, and rebuilding trust can be a challenge.
Legal consequences: Non-compliance with regional regulations can lead to hefty fines and other negative outcomes.
The worst-case scenario can be catastrophic, negatively affecting your business reputation over a long period of time. For example, a popular pizza chain said in September 2023 that it believed about 193,000 customers were affected by a data breach which involved the theft of their personal information. That’s just one example of an Australian business that has seen breaches, and worn the brand damage.
In short, secure payment processing should be seen not as an unwanted financial burden but as an investment in your company’s growth and success.
Stop fraud before it occurs. Integrated payment fraud detection.
What are the key components of payment security?
The world of digital payments is evolving fast; and the sophistication of cyber criminals is growing in tandem with that of cyber security professionals. Ensuring robust payment security is not only a regulatory requirement but also a fundamental aspect of building trust in the digital marketplace. There are three main pillars to a safe payment system. Understanding these will help you choose a payment acquirer that will stand up to attack.
1. Authentication
This is the process of verifying the identity of the parties involved in the transaction – checking, in other words, that customers, merchants and financial institutions are all who they claim to be. A common example of an authentication method used in payment processing is the card verification value (CVV): the three or four-digit code printed on credit and debit cards. During online or phone transactions, customers are often asked to share this code. The idea being that even if a fraudster has obtained a card number, only someone who is in possession of the card will have access to this code.
To reduce the risk of card fraud further, modern payment providers offer multi-factor authentication. This means that, in addition to providing their card details, a cardholder will sometimes be asked to perform a second authentication step before a transaction is processed. For example, a one-time code could be texted to the user or a fingerprint scan could be required.
2. Confidentiality
While authentication is about checking people are really who they say they are, confidentiality is about keeping their information safe. Customer data and card details must be kept private during transmission and storage, and encryption plays an important role in this.
3. Integrity
This third pillar is about the accuracy and trustworthiness of data, ensuring that transactions remain free from tampering throughout the process. A reliable payment acquirer uses methods such as digital signatures and secure data transmission protocols to guarantee the integrity of each transaction. This means that both merchants and customers can rest assured that no information will be altered while they’re not looking.
How does encryption keep payments safe?
Encryption methods are constantly evolving to keep up with increasingly sophisticated threats to security. Two common methods of encryption, which have been used and improved for decades, are SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security).
SSL was developed by Netscape in the mid-1990s to ensure privacy, data integrity and authentication in online communication. It involves a “handshake”, which means that the server sends its digital certificate to the client, and then a cryptographic key is shared. This means that information can be scrambled while in transit, but can be unscrambled when it reaches its destination.
SSL was updated several times in the 1990s to address vulnerabilities, and then TLS was introduced in 1999 as an upgrade. This introduced more features and addressed more vulnerabilities to attack. TLS is still a benchmark for secure communication, and its adoption is widespread in protocols like HTTPS. The encryption algorithms and key exchange methods have continued to evolve over the last couple of decades to meet the growing pressures for online security. Keep in mind that some people still use the term SSL when they mean TLS.
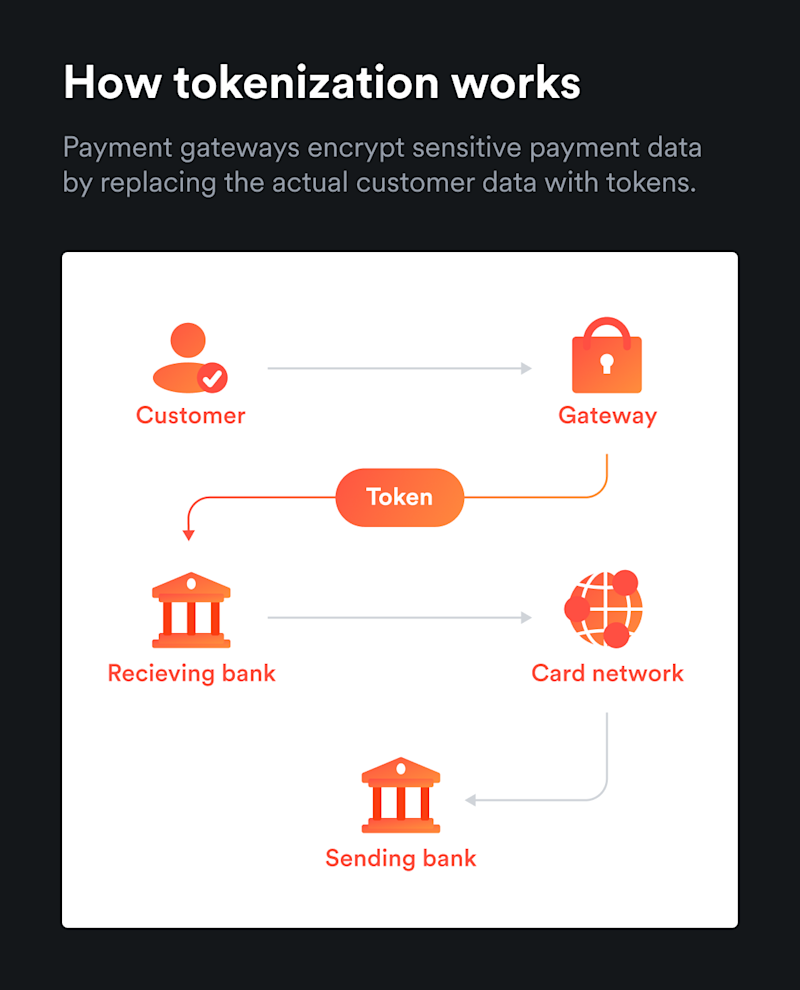
TLS is designed for secure communication over the internet, ensuring that data exchanged is confidential and secure. It ensures no one can eavesdrop or tamper with the information being transmitted. However, it is not the only important concept in modern digital security. Tokenisation is another important innovation, which emerged in the 2000s. It involves replacing sensitive data with a unique identifier or ‘token’ and is important in the realm of credit card payments.
How does tokenisation work and what are the benefits?
While traditional encryption is about scrambling and unscrambling data to make it unintelligible in-transit, tokenisation involves replacing sensitive information (such as credit card information) with non-sensitive, unique tokens. To do this, a secure vault or server is used to generate and manage these tokens. The sensitive data is sent to this repository, and a token represents the information in the transaction process.
This means that even if hackers managed to intercept a token, they would still be unable to use this to access the original information. Tokenisation provides an additional layer of security beyond traditional encryption methods, helping to boost both data confidentiality and integrity.
The PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), which sets security requirements for handling credit card information, has played a significant role in promoting tokenisation since the mid-2000s. Now, tokenisation has become a widely adopted practice. Mobile payments and digital wallets, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, as well as card networks, such as Visa and Mastercard, use tokenisation to enhance the security of payment card information. It is also used to protect sensitive information in other sectors, such as healthcare.
Payment processors and compliance
Many of the features above concern the security of customers and their sensitive data. It’s also important to work with a payment acquirer that protects the company itself. One of the ways it can do this is by ensuring that it adheres to strict compliance standards. A reliable payment processor will be up-to-date with industry standards – and this includes not just those applicable in the company’s home country but also any other territories where business is transacted.
PCI DSS
One global set of standards that merchants and payment providers must adhere to is the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This was designed to ensure the secure handling of credit card information during online transactions and reduce the risk of data breaches and fraud.
PCI DSS is not a law, but a contractual obligation imposed by major credit card companies to organisations that process, store, or transmit credit card information. This includes merchants, payment providers and financial institutions.
Key components of PCI DSS include requirements for:
Building and maintaining a secure network.
Protecting cardholder data through encryption and other security measures.
Implementing strong access control measures.
Regularly monitoring and testing networks for vulnerabilities.
Maintaining an information security policy and ensuring staff are trained on security best practices.
PCI DSS compliance is typically categorised into four levels based on the number of transactions a business processes annually. The larger the volume of transactions, the more rigorous the compliance requirements. Non-compliance can result in financial penalties, restrictions on card processing capabilities, and reputational damage.
Are there different compliance rules around the world?
In addition to PCI DSS, there are other industry standards and regional regulations that companies handling payments should be aware of.
In Australia, we have the Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) Scheme, which obliges companies that experience data breaches to notify authorities.
Elsewhere around the world, compliance rules include;
ISO/IEC 27001: An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS), which deals with the management of sensitive information
GDPR: An EU regulation dealing with the processing of personal data and people’s right to privacy
Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Determines how companies operating in Singapore can collect and use
personal data.
Learn more about Airwallex's PCI DSS compliant payment solutions
What are the advanced security features to look for in a payment provider?
Here are some security features that have reshaped the landscape of digital payment security recently. A reliable payment processor will seamlessly integrate these features to ensure the integrity, authenticity and confidentiality
of online data.
3D Secure
Also known as 3DS, 3D Secure introduces an extra layer of security to payments, in addition to traditional passwords. Users are required to verify their identity a second time, through a measure such as a one-time passcode, redirection to their bank’s authentication page or biometric authentication methods. This reduces the
risk of unauthorised transactions.
In Europe, 3DS is required by the Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) regulation for all card payments, though it is optional in other regions. Some companies might set 3DS to be presented to the customer if the transaction value exceeds a certain number or is considered to be suspicious or risky.
In 2022, major card brands made the switch to an updated version of the 3D Secure protocol, known as 3D Secure 2 (3DS2). This improved upon some of its predecessor’s limitations, enabling faster, more secure and more accurate fraud detection.
Biometric Verification
Fingerprint and iris scans and voice and facial recognition technology are all increasingly being used as an extra layer of authentication in digital payments. Because biometric data is so unique and distinctive, and the technology is now so fast and seamless, it’s a user-friendly way of boosting security.
Machine Learning
Traditional computing is about programming machines to behave in rule-based ways, but machine learning algorithms can evolve and adapt to vast datasets, figuring out what an anomaly looks like. This means they can alert companies to potentially fraudulent, anomalous activities in real time.
A trustworthy payment processor will use all these advances in cybersecurity to serve as a multifaceted defence against evolving threats. The result can be not just stronger security but also a relatively frictionless experience for customers.
How to choose a payment partner
Choosing the right payment provider is a decision you want to get right the first time. Once it’s in place, you should be able to focus on the growth of your company, knowing that your processor will continue to be secure and reliable. It should not only meet your current needs but also provide robust security features for the future.
Here is a checklist of questions to ask as you narrow down the list:
What security measures are in place to protect sensitive customer data? As outlined above, consider end-to-end encryption, tokenisation and compliance with industry standards such as PCI DSS.
Can the payment processor scale with the growth of your business? Think beyond your current transaction volume and ensure the payment provider has the flexibility to cope as your business expands.
Does the payment acquirer support international transactions? Check for support for multiple currencies, local payment methods, and compliance with regional regulations, so that you can expand your business into new markets seamlessly.
How easily can the payment solution integrate with your existing systems? Opt for a solution with seamless API integration and compatibility with popular eCommerce platforms.
What are the pricing models and associated fees? Transparent and competitive pricing with a clear breakdown of fees is crucial for cost management.
Is customer support available around the clock? The ability to reach a support team at any time is crucial, especially in the event of urgent issues or security concerns.
How knowledgeable is the technical support team? Ideally there will be a team with the expertise to quickly resolve issues, minimising disruptions to your payment processes.
Is there comprehensive documentation available for self-directed troubleshooting? This empowers your team to deal with minor issues independently and ensures a smoother integration process.
If you are already working with a payment provider, it’s worth conducting a thorough review to ensure that you have the most powerful, secure solution that’s also cost-effective and easy to use. If there are doubts, consider an upgrade to Airwallex.
Gold-standard payment security with Airwallex
Airwallex offers payment processing and acquiring services for the modern global business, with state-of-the art payment security technology.
Designed with a global-first mindset, Airwallex holds 60+ financial licences in territories across the world. This means compliant, secure and seamless payment acceptance no matter where your customers are based. You can localise your checkout with 160+ payment options, including Apple Pay, Google Pay, Alipay and Klarna. And you can price and settle in multiple currencies whilst avoiding costly foreign exchange fees.
Airwallex employs best-in-class security technology to keep your business and your customers safe, including network tokenisation and 3DS2. Airwallex’s machine learning-powered optimisation engine includes automatic retries, ISO message optimisations, and pre-chargeback programs to help you improve payment acceptance rates and minimise the cost of payment disputes.
With Airwallex, you can feel secure knowing that your customer’s data is protected with new-generation technology. To find out more, sign up to Airwallex today.
Disclaimer: This information doesn’t take into account your objectives, financial situation, or needs. If you are a customer of Airwallex Pty Ltd (AFSL No. 487221) it is important for you to read the Product Disclosure Statement (PDS) for the Direct Services, which is available here.
Share

Izzy is a business finance writer for Airwallex, specialising in thought leadership that empowers businesses to grow without boundaries. Izzy has more than four years of experience working alongside Aussie startups and SMEs, having previously worked at one of the country’s leading HR tech companies. Izzy’s diverse experience across business operations, from people to finance, brings a unique perspective to her current role.
Related Posts
Is Airwallex safe?
•10 min

How to build customer trust with robust payment security
•6 minutes
