How tokenization works and its benefits for online payment security
Security has become a top priority in eCommerce payments, as more people turn to online shopping and rely on digital transactions for their everyday purchases. Merchants are working hard to keep their customers' payment data safe during transactions, while balancing this with providing streamlined and convenient checkout experiences. As worldwide cybercrime costs are estimated to hit $10.5 trillion annually1 in 2025, the need for strong security controls is clear.
With this in mind, let’s examine ‘tokenization’ – the process that enhances the security of online payments and removes customer checkout friction.
What is tokenization?
Payment tokenization is a process used by businesses to better protect the security of customers’ payment data, when a cardholder chooses to save their payment details with the merchant. It involves sensitive payment information, such as credit card numbers, being replaced with ‘tokens’, which are a set of 16 unique random numbers and letters.
One of the important pieces of information that tokenization protects is the primary account number (PAN). The PAN is a unique number that identifies a cardholder's account and the issuer of a credit, debit, or prepaid card. It's a key piece of information that's used to process payments.
With tokenization, the original payment data is stored in a secure vault by the merchant, payment processor, or card network (whoever is handling the tokenization), and a corresponding token is then used instead to process the payment. This means that if someone, such as a hacker, were to access the token, they'd be prevented from using it to make purchases, as the token serves as a placeholder for the sensitive card information but holds no meaning outside its designated ecosystem.
Any merchant accepting digital payments must be compliant with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS). Tokenization can help businesses achieve PCI DSS compliance by minimising risks associated with the storage and transmission of cardholder data. However, many merchants choose to outsource tokenization management to a token service provider (which could be payment processors or payment networks), rather than handling it themselves. This shifts the responsibility for safeguarding the customers' sensitive data during storage to the payment processor or network handling the tokenization.
IBM’s 2023 ‘Cost of a Data Breach Report’2 puts the global average cost of a data breach at US$4.45 million. With sensitive payment information stored in secure vaults, tokenization helps protect against fraudulent activity by removing the ability for hackers to access cardholder information as it is used in online transactions.
Tokenization is used by all types of businesses, including platforms and marketplaces, subscription-based services, eCommerce retailers, and physical stores to dramatically enhance customer security and streamline the management of payment data.
How does tokenization work?
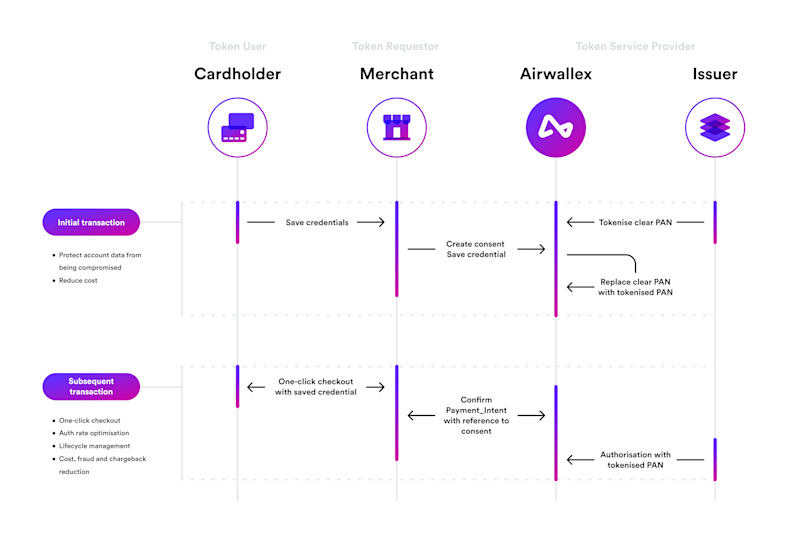
Here’s what happens during the tokenization process.
Cardholder enters information: A customer uses their credit card for an online transaction and chooses to ‘save’ their payment data with the merchant.
Tokenization occurs: The credit card number is sent to a secure tokenization system and stored in a vault. The system generates a unique token for the cardholder, which is a string of 16 random characters that replace the original credit card number.
Replacement: The newly generated token is returned to the merchant or system that initiated the payment to replace the credit card number within that system.
Verification: When a transaction is processed, the token is sent to the payment processor, who maps it back to the original credit card information for verification.
Tokenization example
When a merchant processes a customer’s credit card information, the credit card number is replaced with a unique token. 1234-5678-1234-5678 is replaced with, for example, 4!sf%gS68kfUa3fp. The merchant stores the token ID to retain records of the customer. For example, 4!sf%gS68kfUa3fp is connected to the customer, Diane Williams.
The benefits of tokenization in online payment security
Improving data security and preventing fraud
Tokenization improves data security by replacing sensitive information (that hackers could steal and use to make purchases) with non-sensitive tokens which have no intrinsic value. As a result, even if hackers gain access to a token, they can't access or misuse the original data.
Using tokenization also simplifies data management overall, as the tokens can be used over multiple systems without storing the sensitive data in various locations. Overall, tokenization minimises exposure, reducing the risk of data breaches and allowing businesses to protect customer data while also streamlining their transaction functionality.
Simplifying PCI DSS compliance requirements
Tokenization reduces the scope of PCI-DSS compliance by reducing the number of virtual locations where sensitive data is held. When businesses outsource tokenization to a payment processor or card network, it reduces their burden of handling sensitive data, meaning they face less complexity in meeting security requirements, reducing the need for expensive audits, while lowering their risk of non-compliance.
Fostering customer trust
Whether a business uses tokenization or not isn't usually public knowledge. However, customers trust (and want to buy from) companies that demonstrate a commitment to data security. Merchants without security breaches will also have better reputations, fostering loyalty from their customers. Displaying various security accreditations at checkout can also increase credibility and sales.
As well as increasing trust, tokenization makes it easier for customers to purchase from their favourite businesses. Tokens streamline payments for repeat customers, which can increase conversions. For example, with the option to securely save payment information, customers won’t need to re-enter their payment details each time they check out, or for recurring payments and subscriptions.
How does tokenization fit within payment security processes
Tokenization is just one part of a multi-layered security strategy that all businesses accepting payments should implement. Encryption, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and fraud detection systems are additional security processes that merchants often employ, and work with tokenization to ensure the integrity of transactions. Together, these technologies strengthen a business’s overall payment security and mitigate risk, as well as creating a better experience for customers.
Beyond the payment security process, tokenization improves the chance of repeat purchases and subscription sales by eliminating the need for customers to re-enter their financial information, streamlining future transactions. Merchants benefit from faster checkouts and improved customer retention, while customers enjoy a seamless, convenient, and secure purchasing experience that can encourage them to purchase again and again.
Airwallex: a secure choice for payments
Airwallex’s modern financial platform is designed to help you grow and protect your global revenue. We have tokenization built-in to our Payments solution, making it easier than ever for you to integrate the payment security measures you need.
Our full-stack Payments platform directly integrates with all major card networks and allows customers to make payment via 160+ local payment methods. Explore how our secure payment processing solutions can help to boost your conversion rates with a truly frictionless checkout experience for your customers.
Support 160+ payment methods. Securely process payments in 130+ currencies.
Source
1. https://www.esentire.com/resources/library/2023-official-cybercrime-report
2. https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach
Share

Shermaine spearheads the development and execution of content strategy for businesses in Singapore and the SEA region at Airwallex. Leveraging her extensive experience in eCommerce, digital payment solutions, business banking, and the cross-border industry, she provides invaluable insights that guide businesses through the complexities of global commerce. Specialising in crafting relevant and engaging content that resonates with business owners, her work is designed to drive growth and innovation within the fintech and business economy space.
View this article in another region:Europe - EnglishEurope - NederlandsUnited KingdomGlobal
Related Posts
Understanding PCI DSS and why it matters
•5 minutes

What is 3D Secure authentication?
•5 minutes
